Sorsogon
| Sorsogon | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| — Province — | |||
|
|||
 |
|||
| Coordinates: | |||
| Country | |||
| Region | Bicol Region (Region V) | ||
| Founded | October 17, 1894[1][2] | ||
| Capital | Sorsogon City | ||
| Government | |||
| - Governor | Raul Lee (Lakas-Kampi-CMD) | ||
| Area | |||
| - Total | 2,119.0 km2 (818.2 sq mi) | ||
| Area rank | 61st out of 80 | ||
| Population (2007) | |||
| - Total | 709,673 | ||
| - Rank | 35th out of 80 | ||
| - Density | 334.9/km2 (867.4/sq mi) | ||
| - Density rank | 16th out of 80 | ||
| Divisions | |||
| - Independent cities | 0 | ||
| - Component cities | 1 | ||
| - Municipalities | 14 | ||
| - Barangays | 541 | ||
| - Districts | 1st and 2nd districts of Sorsogon | ||
| Time zone | PHT (UTC+8) | ||
| ZIP Code | |||
| Spoken languages | Bikol | ||
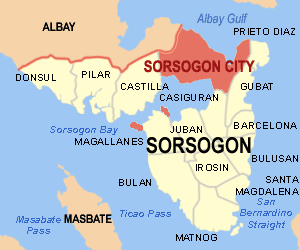
Sorsogon is a province of the Philippines located in the Bicol Region; it is the southernmost province in Luzon and is subdivided into fourteen municipalities (towns) and one city. Its capital is Sorsogon City (formerly the towns of Sorsogon and Bacon) and borders the province of Albay to the north. Sorsogon is at the tip of the Bicol Peninsula and faces the island of Samar to the southeast across the San Bernardino Strait and Ticao Island to the southwest.
Contents |
History
Ferdinand Magellan’s death in 1521, in the hands of Lapu-lapu did not stop the Spanish colonization of the Philippine Islands. In 1570 two Augustinian friars, Fr. Alonzon Jimenez and Fr. Juan Orta, accompanied by a certain Capt. Enrique de Guzman, reached Hibalong, a small fishing village near the mouth of Ginangra River in Magallanes and planted the cross and erected the first chapel in Luzon. It was from this village that Ibalong, referring to the whole region came to be. Moving inland with a northwesterly direction they passed by the territory now known as Pilar, before they reached Camalig, Albay. The establishment of the Abucay-Catamlangan Mission later was ample proof of this route.
Sorsogon was once a part of Albay, which also included the province of Masbate. The early towns established here were: Gibalon in 1570 (now sitio of Magallanes); Casiguran -1600; Bulusan – 1631; Pilar – 1635; Donsol – 1668; Bacon – 1764; Juban and Matnog - 1800; Bulan - 1801; Castilla – 1827; Magallanes – 1860; Sorsogon – 1866 and Irosin – 1880. The province was eventually separated from Albay on October 17, 1894 and adopted the name Sorsogon. The town of Sorsogon was also selected as its capital.[1]
On 1935 Philippine Constitutional Convention, Sorsogon had its own delegates. They were Adolfo Grafilo, Francisco Arellano, Jose S. Reyes and Mario Guarino.
Geography
Sorsogon, at the southeastern part of the Bicol Peninsula, is bounded on the north by the province of Albay, on the east by the Philippine Sea, on the south by the San Bernardino Strait, and on the west and northwest by the Ticao and Burias Passes. It has a total land area of 2,119 km2.
It is characterized by an irregular topography, and, except for landlocked Irosin, all the towns lie along the coast. They are all connected by concrete and asphalt roads. Mountains sprawl over the northeast, southeast and west portions. Mt. Bulusan, the tallest peak, rises 1,560 meters above sea level.
Except for its overland link with the province of Albay to the north, it is completely surrounded by water. Sorsogon is the gateway of Luzon to the Visayas and Mindanao through its Roll-on/Roll-off ferry terminal facilities located in the municipalities of Matnog, Pilar and Bulan.
Economy
The province's economic activity is highly concentrated in its capital city, Sorsogon City, and the towns of Bulan, Irosin, Gubat, and Matnog as well. Sorsogon Province is classified as 2nd class with an average annual income of ₱339.4M (C.Ys. 2000-2003). This is about ₱11M short for the province to attain 1st class reclassification which requires at least ₱350M average annual income.
The Province of Sorsogon indeed had a great contribution on the 97-percent growth in investments for the first quarter of 2008 and increasing tourism arrivals that buoyed the Bicol Region economy, despite the damage brought about by incessant rains and a rice shortage. This is according to the Quarterly Regional Economic Situationer (QRES) released by the National Economic and Development Authority (NEDA) Regional Office in Bicol (NRO 5).
Among the provinces, Sorsogon posted the highest growth (293% respectively) in investments from the previous year. Next to Sorsogon is Catanduanes that posted a growth of 280%. Albay contributed 39 percent to the region's investments and posted a growth of 221% from the preceding quarter.
“For the third time, Bicol Region hosted the kick-off of Asia's premier extreme sailing event, the Philippine Hobie Challenge last February 16 at Gubat, Sorsogon. This 260-mile journey from Gubat-Sambuyan-Bacsal-Marambut-Suluan[3] to Siargao enticed both local and foreign water sports enthusiasts. It opened the opportunity for the municipality of Gubat to showcase the town's best,” the QRES stated.
People and culture
Festivals
- Town Fiestas
Most of the inhabitants of the province belong to the ethnolinguistic Bicolano and Bisakol groups. Sorsogueños - as how the people of Sorsogon call themselves - are very religious and fun-loving. Being mostly Roman Catholics, they are active in every festivity celebrated throughout the year. Like any other Filipino ethnolinguistic groups, each town honors their Patron Saint with celebration on its Feast Day. In Sorsogon City, the locals celebrate the Fiesta of the Patron Saints Peter and Paul in June 28-29 of each year. Another featured attractions during town fiestas are the Traveling carnivals that sets up near the town center or its vicinities.
- Kasanggayahan Festival
The festival, celebrated in the whole province in the last week of October, commemorates the founding of Sorsogon as a province. Festivities include a series of cultural, historical, religious, agro-industrial and economic activities, showcasing the province’s abundant agricultural products, particularly food and decorative items.
- Pili Festival in Sorsogon City honors the Pili nut and tree which is indigenous to province. The festival coincides with the town fiesta of Sorsogon City. Celebrations include street dancing by locals donning pili nut costumes, cooking competitions, fireworks displays, and even a nutcracking session along the road by the locals.[4]
Minorities
Minorities include Muslim immigrants from Mindanao, who engage in street vending and small shop businesses. A mosque is situated inside Sitio Bolangan on the outskirts of the city. A significant small Chinese population are owners of hardware stores and commodity shops and dwell in the business center. Indian communities are also present and are Hindus. They are typically known to engage in money lending businesses—colloquially called "five-six".
Education and language
Education is highly valued as an investment for the future, as illustrated by the many state and private schools and colleges which dot the province. Almost all people understand Tagalog and Bicolano. The local language spoken by Sorsogueños varies from district to municipalities. To illusrate, the form of Bisakol (called Waray Sorsogon) spoken in Barcelona, Gubat, Irosin, Sta. Magdalena, Matnog and Bulusan slightly differs from the form (called Masbate Sorsogon) spoken in the city of Sorsogon and the municipalities of Magallanes, Juban and Casiguran. North of Sorsogon City, in Castilla, Pilar and Bacon (merged with Sorsogon city; see History), a form of Bikol is spoken. Also a different form of Bikol called Miraya similar to that of Daraga, Albay, is spoken in Donsol and some parts of Pilar. The former municipalities mentioned use words and intonations from Visayan languages such as Waray-Waray, Cebuano and Ilonggo, and Bisakol is considered a Warayan language like Waray-Waray of Samar and Leyte. English is also understood by most educated people. It is used in all government documents, schools, and in business. This language has also become increasingly important as businesses such as call centers and medical transcription require prospective applicants to be proficient in it.
Political
Sorsogon is subdivided into 14 municipalities and 1 city. Albay Gulf lies to the north, Ticao Pass between Sorsogon and Ticao Island, and San Bernardino Strait in the south.
| City/Municipality | No. of Barangays |
Area (km²) |
Population (2000) |
Mayor |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barcelona |
|
|
|
||
| Bulan |
|
|
|
|
|
| Bulusan |
|
|
|
||
| Casiguran |
|
|
|
||
| Castilla |
|
|
|
||
| Donsol |
|
|
|
|
|
| Gubat |
|
|
|
||
| Irosin |
|
|
|
||
| Juban |
|
|
|
||
| Magallanes |
|
|
|
||
| Matnog |
|
|
|
||
| Pilar |
|
|
|
||
| Prieto Diaz |
|
|
|
||
| Santa Magdalena |
|
|
|
||
| Sorsogon City |
|
|
|
|
|
Post 1986 people power uprising
In 2000, the municipalities of Bacon and Sorsogon was merged to create Sorsogon City.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 History of Sorsogon. Official Website of the Government of Sorsogon. Retrieved on 2010-06-06
- ↑ Sorsogon, Where Comes the World's Largest Fish. The Philippines Agribusiness Center. Retrieved on 2010-06-06.
- ↑ Philippine Hobie Challenge Wiki.Alumni.NET, Accessed August 2008.
- ↑ Festivals in Sorsogon. Sorsogon Tourism Website. Retrieved on 2010-06-06.
- ↑ NSCB - 2001 Factsheet - 12 New Cities Created, July-December 2000.
External links
|
||||||||